A Step-by-Step Breakdown of Serial Communication – It Doesn’t Get Simpler Than This!

Serial communication, also known as serial transmission, is a short-distance, point-to-point data transfer method. It is based on serial communication protocols and connects devices via serial cables to exchange information. Serial ports are widely used in many hardware systems and are an important interface for communication between industrial computers, microcontrollers, and peripheral devices.
So how exactly does serial communication work? Let’s walk through a straightforward example. Suppose Device A and Device B are connected via a serial cable. Now Device A wants to send the data “12345” to Device B. Here is how the serial port would step-by-step process and transmit this data:
First step – Overall packaging: Device A packages the data to be sent, “12345”, into one overall unit, adding the necessary control information just like packing a parcel to be shipped. The control information here is like a filled out shipping label, containing vital parameters – sender address, receiver address, data length, etc.
Second step – Character separation: Device A splits the overall packaged data into individual characters, according to serial protocol rules, with each 8 bits as one character. For example, “12345” would be divided into multiple 8-bit sequences. This process is like taking items out of a large box and neatly laying them out.
Third step – Serial transmission: Since the serial port has only one sending data line, it cannot transmit multiple bits in parallel. Device A will transmit the divided characters in a pre-set baud rate, starting from the first bit, serially in order. Just like a restaurant server who can only carry one plate at a time with one hand.
Fourth step – Serial reception: Correspondingly, Device B will also use the single-line serial method, synchronized by the clock signal, to receive the characters sent from Device A one bit at a time according to the set baud rate. It sequentially fills the received characters into its own buffer, like a server bringing up plate after plate.
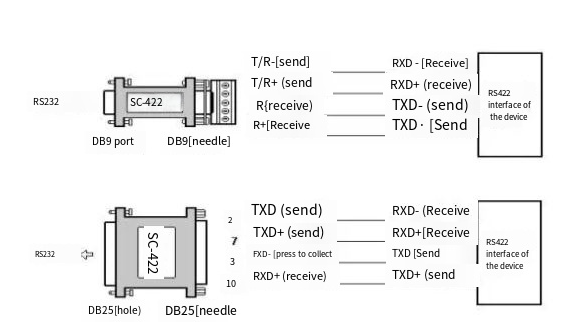
Fifth step – Repackaging: Device B will check and parse all the received characters, organize the relevant control characters and data back together, restoring them into the complete data package originally sent by Device A. This process is like a courier receiving a shipped parcel, checking the tracking number, counting the items, then packing it up for storage.
After going through these steps, the basic serial communication sending and receiving process is complete. Each serial communication will execute these procedures in sequence, ultimately achieving point-to-point data transfer between devices. Understanding this principle will enable us to better grasp debugging and applying serial communication.
 KEY-IOT
KEY-IOT




