A Deep Dive into Industrial Router WiFi Interfaces: From Novice to Expert

Hey folks! I’m Lao Li, and I’ve been working in industrial automation for over a decade. I’ve dealt with my fair share of networking equipment, and I’ve picked up a thing or two along the way. Today, let’s talk about industrial router WiFi interfaces – a topic that can be deceptively simple, yet surprisingly nuanced.Many newcomers to industrial networking might think, “WiFi is just WiFi, right? As long as my phone can connect, it’s all good.”
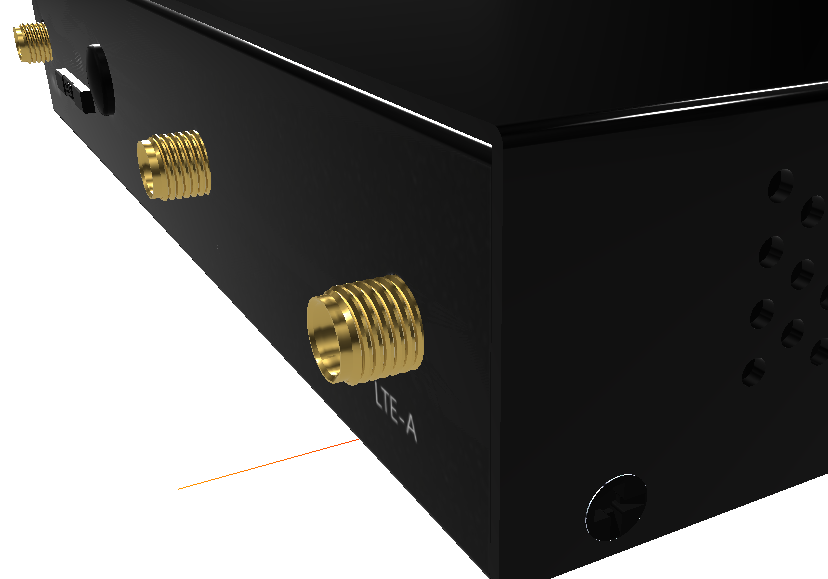
But in the rough and tumble world of industrial environments, things aren’t so straightforward. Factory floors are teeming with electromagnetic interference that would make a hurricane blush. Consumer-grade routers simply crumble under these conditions, dropping connections, lagging, and generally throwing a digital tantrum.So, to conquer the WiFi wild west of industrial settings, you need specialized, rugged equipment. This is where industrial-grade routers come in, and their WiFi interfaces are the unsung heroes of reliable connectivity.1. Interface Types: A Connector for Every OccasionFirst up, let’s talk connectors – those little guys that actually let you plug your antenna in. The most common types you’ll encounter in industrial WiFi routers are RSMA, SMA, and N-type, each with its own strengths and ideal use cases:
- RSMA connectors: These bad boys are built tough with superior interference resistance. Like a router wearing a Faraday cage, they excel in electrically noisy environments packed with heavy machinery, motors, and variable frequency drives.
- SMA connectors: Compact and easy to install, these are the Lego bricks of the connector world. They’re perfect for space-constrained applications where every millimeter counts.
- N-type connectors: The workhorse of the bunch, N-type connectors offer a good balance of performance and versatility, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial settings.
 Of course, there are other, less common connector types like TNC and BNC, but we won’t delve into those today.2. WiFi Protocols: Keeping Pace with ProgressWith the connector sorted, let’s move on to WiFi protocols. Like smartphones, WiFi technology has evolved rapidly, from the early days of 802.11b to the current state-of-the-art WiFi 6 (802.11ax). Each generation brings faster speeds, greater range, and enhanced capabilities.Currently, the two most prevalent WiFi protocols in industrial routers are WiFi 5 (802.11ac) and WiFi 6 (802.11ax):
Of course, there are other, less common connector types like TNC and BNC, but we won’t delve into those today.2. WiFi Protocols: Keeping Pace with ProgressWith the connector sorted, let’s move on to WiFi protocols. Like smartphones, WiFi technology has evolved rapidly, from the early days of 802.11b to the current state-of-the-art WiFi 6 (802.11ax). Each generation brings faster speeds, greater range, and enhanced capabilities.Currently, the two most prevalent WiFi protocols in industrial routers are WiFi 5 (802.11ac) and WiFi 6 (802.11ax):
- WiFi 5 (802.11ac): As the most widely deployed WiFi standard, it offers a sweet spot of speed, coverage, and affordability, making it an excellent choice for most industrial applications.
- WiFi 6 (802.11ax): This is the latest and greatest WiFi protocol, boasting blazing-fast speeds, ultra-low latency, and support for a multitude of devices. Think of it as the information superhighway of WiFi, purpose-built for the bandwidth-hungry demands of Industrial IoT. However, this cutting-edge performance comes at a premium price.

3. Antenna Quantity and Transmit Power: The Secret Sauce of Signal StrengthNow that we’ve covered connectors and protocols, let’s talk about antenna quantity and transmit power – the two factors that determine how far and strong your WiFi signal will reach.
- Antenna quantity: Like having multiple eyes, more antennas mean wider coverage, fewer dead zones, and a stronger overall signal.
- Transmit power: Think of this as the loudness of your router’s voice. Higher transmit power enables the signal to penetrate walls, machinery, and other obstacles, but it also increases power consumption and the potential for interference with other devices.
Therefore, choosing the right antenna quantity and transmit power requires careful consideration of your specific needs, balancing coverage, signal quality, power consumption, and interference potential.4. Sweat the Small Stuff: Don’t Overlook the DetailsBeyond the main factors we’ve discussed, there are a few other details worth paying attention to:
- Ingress Protection (IP) rating: Industrial environments are harsh, often exposed to dust, moisture, and even the occasional splash of oil. Choose connectors with a high IP rating to ensure your router can withstand these environmental hazards.
- Operating temperature range: Industrial settings can experience extreme temperatures, from scorching summers to freezing winters. Make sure your router can handle the heat (or lack thereof) by checking its operating temperature range.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) support: PoE allows you to power your router through the same Ethernet cable that carries data, simplifying installation and reducing cable clutter. If you need to power your router over long distances, look for PoE support.
In conclusion, selecting the right WiFi interface for your industrial router is more than just glancing at a spec sheet. It requires a holistic understanding of your specific requirements and a careful consideration of the factors we’ve discussed. By choosing wisely, you can build a robust and reliable industrial wireless network that can withstand the rigors of any factory floor.And that’s a wrap! I hope you found this helpful. If you have any questions, feel free to ask away.
 KEY-IOT
KEY-IOT
 Of course, there are other, less common connector types like TNC and BNC, but we won’t delve into those today.
Of course, there are other, less common connector types like TNC and BNC, but we won’t delve into those today.