Industrial router project application (4g+5g industrial router project introduction)
364Industrial router
View detailsSearch the whole station 4G Industrial Router Products
With the advancement of technology, wireless communication has significantly improved and rapidly expanded, especially in recent years with the development of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT has penetrated both consumer and industrial sectors. Different wireless communication methods vary in terms of networking, power consumption, communication range, security, and stability, thus finding applications in diverse scenarios. Currently, the most common wireless communication methods in industrial IoT include WiFi, NB-IoT, LoRa, ZigBee, and 4G.
WiFi, based on the IEEE 802.11 protocol, is a technology that allows WiFi-enabled devices to connect to a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). Most WiFi versions operate in the 2.4GHz unlicensed band, with a transmission range of up to about 650 feet, depending on the environment. The popular 802.11n standard can reach speeds of 300Mbps, while the newer 802.11ac, operating in the 5GHz ISM band, can exceed 1.3Gbps. Many factories now have dedicated WiFi networks, making it a recommended choice for such environments. WiFi offers advantages like low cost and high speed.
NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet of Things) is a cellular-based narrowband IoT technology that can be deployed directly on GSM, UMTS, or LTE networks to reduce deployment costs and achieve smooth upgrades. It’s an emerging technology in the IoT field, with China already in large-scale commercial use, especially in water and gas meter industries. NB-IoT features low power consumption and low BOM costs but incurs operational fees and requires network coverage by carriers.
LoRa (Long Range) is a low-power, narrow-band, long-distance communication technology based on spread spectrum technology, introduced by Semtech Corporation. LoRa uses linear frequency modulation spread spectrum technology, spreading energy into noise, and can recover signals even 25dB below noise level. It increases communication distance and network efficiency while maintaining low power consumption. LoRa offers advantages like low cost, long-range communication, and flexible network deployment, but has slower communication rates and requires self-built networks.
ZigBee, based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, is a short-range, low-power, low-cost wireless self-networking communication technology. In the U.S., ZigBee mainly operates in the 2.4GHz band with 16 channels and a theoretical communication rate of 250kbps. ZigBee’s network topology includes star and mesh networks, with self-networking and self-healing capabilities, enabling multi-level relay communication services. Its features include low power consumption, self-networking, and support for numerous nodes. Due to its 2.4GHz operation and limited transmission power, ZigBee’s communication range is typically within 300 feet.
4G communication technology is the fourth generation of mobile information systems, with Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) being the most prominent. It enables wireless communication services like Wireless Local Loop (WLL) and Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB). In smart communication devices, 4G technology allows users to achieve internet speeds of up to 100Mbps. For industrial applications, 4G offers wide signal coverage and high speeds but its higher costs, power consumption, and operational fees make it less suitable for small sensors and more appropriate for larger concentrators or smart terminal devices.
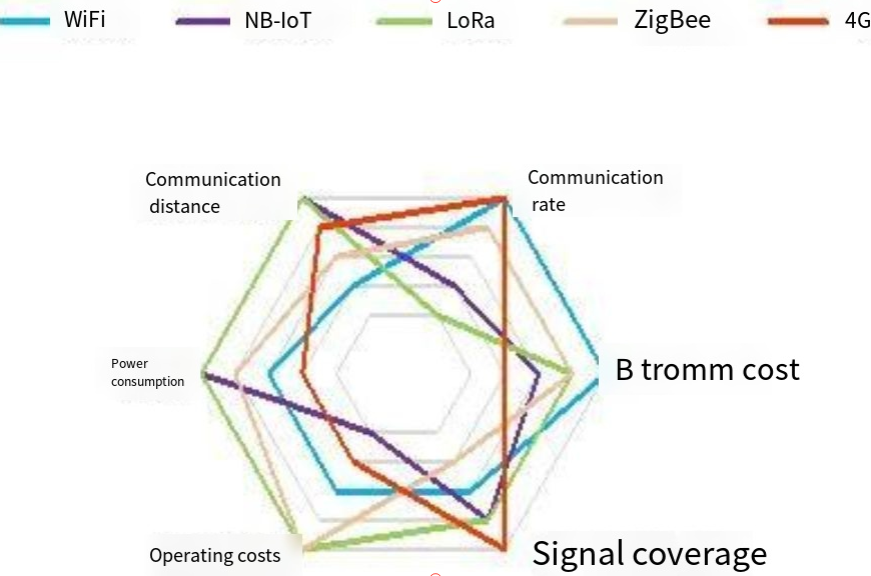
In conclusion, each communication technology has its strengths and inevitable weaknesses. To visualize these differences, we can use a hexagonal diagram with six angles representing communication distance, communication rate, power consumption, BOM cost, operational cost, and signal coverage range. The closer a point is to the outer tip of the hexagon, the more advantageous that aspect is. For example, LoRa communication has a cost advantage as it doesn’t incur operational fees, while NB-IoT and 4G communications don’t have this advantage.
How LTE Modems Are Leveling Up Data Security with VPN TechHey there, tech fans! In this wild world of the Internet of Things, keeping our data safe is a big freakin' deal. LTE modems are these cool wireless gadgets that send data over cellular net...
View detailsThese bad boys are speed demons!With their high-performance CPUs, industrial routers can handle data several times faster than your average router. This means more people can connect at once, and the signal can reach farther than ever before.
View detailsIn conclusion, I want to emphasize that optimizing network slice configurations for 4G industrial routers in large-scale Industrial IoT deployments is an ongoing process.
View details