![[pics:title]](https://www.key-iot.com/static/upload/image/20240522/1716340611714958.png)
In this age of internet of things, 4G LTE technology has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. And behind this technology, the 4G LTE modem plays a crucial role. This article will unveil the mysteries of the 4G LTE modem, delving deep into its working principles and key technologies, so we can appreciate together this core engine of the mobile communications world.
1. What is a 4G LTE Modem?
Imagine the 4G LTE modem as a translator fluent in multiple languages. Its main task is to “translate” between digital devices and cellular networks. Simply put, the 4G LTE modem converts digital signals from devices into wireless signals that can be transmitted over cellular networks, and vice versa. This seemingly simple process actually involves many complex technologies and intricate operations.
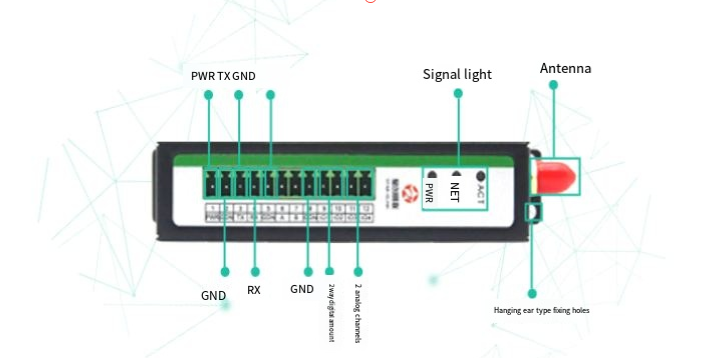 2. How 4G LTE Modems Work
2. How 4G LTE Modems Work
Let’s follow the journey of a data packet to understand how 4G LTE modems work:
1. Signal Modulation:
When your device needs to send data, the 4G LTE modem first converts the digital data into analog signals. This process is like translating text into Morse code, using a technology called OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access). OFDMA is like an efficient postal system, handling multiple parcels (data) simultaneously, greatly improving transmission efficiency.
2. Radio Frequency Conversion:
The modulated signal is then converted into a high-frequency radio signal. This is like putting our “Morse code” into a high-pitched loudspeaker that can propagate over long distances. The RF front-end in the 4G LTE modem handles this process, containing components like power amplifiers, filters and antenna switches.
3. Signal Transmission and Reception:
The converted RF signal is transmitted through the antenna into the cellular network. When receiving data, this process is reversed. The 4G LTE modem’s antenna system typically uses MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology. This is like equipping our “translator” with multiple ears and mouths to listen and speak in multiple languages simultaneously, greatly enhancing communication efficiency.
4. Signal Demodulation:
The received RF signal, after being amplified and filtered, is demodulated back into the original digital data. This is like translating the received “Morse code” back into text. The 4G LTE modem uses advanced signal processing algorithms, like channel estimation and equalization, to accurately recover the original data.
5. Protocol Handling:
Finally, the 4G LTE modem needs to handle various complex communication protocols. This is like adhering to international diplomatic etiquette to ensure smooth communication with the network. This includes signaling, security authentication, resource allocation, etc.
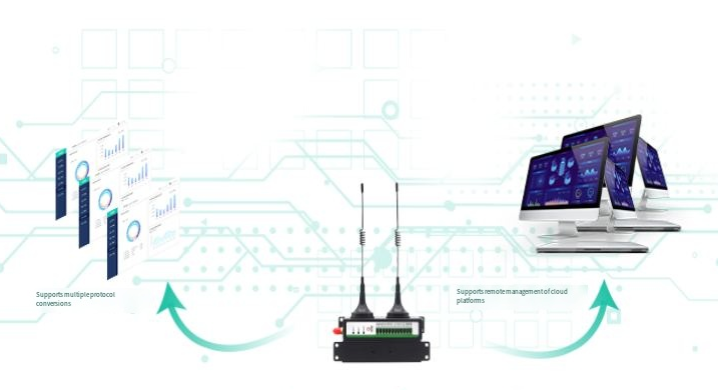 3. Key Technologies of 4G LTE Modems
3. Key Technologies of 4G LTE Modems
1. OFDMA and SC-FDMA:
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) are the core multiple access technologies of 4G LTE. OFDMA is mainly used for downlink while SC-FDMA is used for uplink. These two technologies are like efficient traffic systems, allowing multiple users to share spectrum resources simultaneously, greatly increasing network capacity and efficiency.
2. MIMO Technology:
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology is another weapon in the 4G LTE modem’s arsenal. By using multiple antennas for concurrent transmission and reception, MIMO significantly increases data transfer rates and reliability. This is like adding multiple lanes to a busy highway, improving traffic efficiency and safety.
3. Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC):
AMC allows the 4G LTE modem to automatically adapt modulation schemes and coding rates based on channel conditions. This is like a smart driver adjusting speed and route based on road conditions to ensure efficient and stable data delivery under various circumstances.
4. Carrier Aggregation:
Carrier aggregation enables the 4G LTE modem to use multiple frequency bands for data transmission concurrently. This is like aggregating multiple small streams into one big river, greatly enhancing data rates. The latest 4G LTE Advanced Pro supports aggregation of up to 32 carriers, with theoretical peak rates up to 3Gbps.
5. Low Power Technologies:
For mobile devices, power consumption has always been a critical issue. 4G LTE modems adopt various low power technologies like dynamic power control and sleep modes. This is like installing an intelligent power management system for our “translator” to automatically enter energy saving mode when not working, significantly extending device battery life.
6. Security Encryption:
During data transmission, security is paramount. 4G LTE modems employ multi-layered security mechanisms including identity authentication and data encryption. This is like encasing our communications in a sturdy protective shield, effectively preventing eavesdropping and tampering.
 4. Future Outlook
4. Future Outlook
With the advent of the 5G era, 4G LTE modems continue to evolve. The latest LTE Advanced Pro technologies are converging with 5G NR (New Radio), with significant improvements in data rates, latency and connection density. In the future, 4G and 5G will coexist long-term, and 4G LTE modems will continue to play vital roles in IoT, vehicle networking and other fields.
 KEY-IOT
KEY-IOT![[pics:title]](https://www.key-iot.com/static/upload/image/20240522/1716340611714958.png)
 2. How 4G LTE Modems Work
2. How 4G LTE Modems Work 3. Key Technologies of 4G LTE Modems
3. Key Technologies of 4G LTE Modems 4. Future Outlook
4. Future Outlook


