In modern industrial sectors, data acquisition, transmission, and processing are crucial for achieving automation and intelligence. Ethernet, as a mature and widely used network technology, plays an increasingly important role in industrial environments. The Ethernet interface of industrial routers is a key component for connecting industrial devices and networks. This article will delve into the basic concepts and standards of Ethernet, as well as its unique advantages and applications in the industrial field.
I. Basic Concepts and Standards of Ethernet
Ethernet is a local area network (LAN) technology based on the CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) mechanism, developed by Xerox Corporation in the 1970s. After years of development and refinement, Ethernet has become one of the most mainstream wired network standards. Ethernet can be divided into multiple standards according to transmission rate and media type, such as 10Base-T, 100Base-T, and 1000Base-T.
– 10Base-T: An early Ethernet standard with a transmission rate of 10Mbps, using twisted pair cable as the transmission medium.
– 100Base-T: Also known as Fast Ethernet, it has a transmission rate of 100Mbps and still uses twisted pair cable.
– 1000Base-T: A type of Gigabit Ethernet with a transmission rate of 1000Mbps (1Gbps), using Cat5e or higher-grade twisted pair cable.
In addition to transmission rates, Ethernet also defines different physical layer and data link layer protocols, such as IEEE 802.3, to ensure interoperability between devices.
II. Differences between Industrial Ethernet and Regular Ethernet
Although industrial Ethernet and regular Ethernet are based on the same standards, industrial Ethernet takes into account the special requirements of industrial environments in its design and implementation, which is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Environmental Adaptability: Industrial Ethernet devices often need to adapt to harsh industrial environments, such as wide temperature ranges, strong vibrations, high humidity, and corrosive gases. Therefore, industrial Ethernet devices are more robust and durable in their mechanical and electrical design.
2. Real-time Performance and Determinism: Industrial control systems have high requirements for real-time performance and determinism of data transmission. Industrial Ethernet ensures low-latency and reliable data transmission by introducing real-time Ethernet protocols (such as EtherCAT, PROFINET, etc.) and optimized network topologies.
3. Redundancy and Fault Tolerance: To improve system reliability, industrial Ethernet often adopts redundant designs, such as dual networks and dual power supplies, to ensure that the system can continue to operate normally in the event of a single point of failure.
4. Security: Industrial networks face more security threats, such as unauthorized access and malicious attacks. Industrial Ethernet devices typically integrate more powerful security features, such as firewalls, VPNs, and access control, to protect critical industrial assets.
III. Advantages of Ethernet in Industrial Environments
Ethernet is increasingly widely used in industrial fields, mainly due to the following advantages:
1. Openness and Interoperability: Ethernet is an open standard that supports a variety of industrial protocols and application layer protocols, such as Modbus TCP and OPC UA. This allows devices from different manufacturers to be easily integrated into the same network, achieving interconnectivity and interoperability.
2. High Bandwidth and Scalability: With the increasing intelligence of industrial devices and the growth of data volume, Ethernet provides sufficient bandwidth to meet the needs of data transmission. At the same time, Ethernet networks can be easily expanded by adding new devices and switches.
3. Remote Access and Maintenance: Through Ethernet, engineers can remotely access and configure industrial devices, perform fault diagnosis and maintenance, greatly improving the operational efficiency of the system.
4. Cost-effectiveness: Ethernet technology is already very mature, and the costs of related hardware and software continue to decrease. Compared with other industrial network technologies, Ethernet provides better cost-performance ratio.
IV. Differences between Industrial Ethernet Switches and Routers
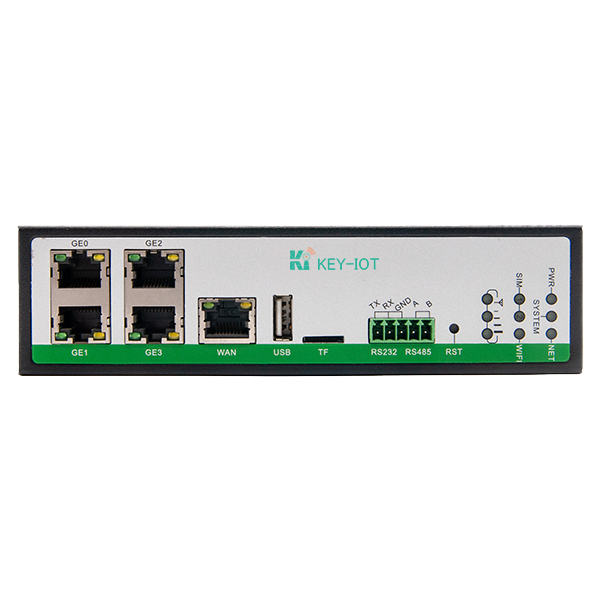

In industrial Ethernet networks, switches and routers are two common types of devices, and they differ in function and application:
1. Industrial Ethernet Switches: Mainly working at the data link layer (Layer 2 of the OSI model), responsible for forwarding and filtering data frames. Switches use MAC address tables to determine the destination port for forwarding data frames, while also isolating collision domains and improving network efficiency. Industrial Ethernet switches typically support functions such as VLAN, QoS, and IGMP Snooping for network segmentation and optimization.
2. Industrial Ethernet Routers: Working at the network layer (Layer 3 of the OSI model), mainly responsible for forwarding and routing data packets between different networks. Routers use IP addresses and routing tables to determine the next hop destination for data packets. Industrial routers typically integrate more advanced features such as VPN, firewall, and NAT for secure network interconnection and remote access.
In practical applications, switches are mainly used to build LANs and connect devices within the same network segment, while routers are used to connect different network segments or subnets, achieving wide area network interconnection. The combination of both can build efficient, reliable, and secure industrial Ethernet networks.
V. Conclusion
With its advantages of openness, high bandwidth, and scalability, Ethernet has become the mainstream choice for industrial networks. The Ethernet interface of industrial routers plays a vital role in achieving reliable connections between industrial devices and networks. By gaining an in-depth understanding of the basic concepts, standards, characteristics, and application advantages of industrial Ethernet, we can better design and deploy industrial networks to promote the digitalization and intelligent development of industrial systems. At the same time, correctly understanding and using industrial Ethernet switches and routers is also crucial for building high-performance, secure, and reliable industrial networks.
 KEY-IOT
KEY-IOT




